고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
문제 상황
const asyncFunc = async (id: number): Promise<string> => {
try {
// get data with id
const {data} = await axios.get(`https://example.com?id=${id}`);
return data.name;
} catch (e) {
// catch...
}
}id를 parameter로 받아와, string을 반환해주는 비동기 함수 asyncFunc가 있다.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]위의 배열의 값으로 asyncFunc에서 값을 받아와 배열을 만드려고 한다.
const brr = arr.map((id) => asyncFunc(id));
console.log(brr);하지만 위처럼 코드를 쓰고 콘솔에 `brr`를 찍어보면 아래와 같다.
console
[Promise { < pending > }, Promise { < pending > }, Promise { < pending > } ...]이런 pending(대기) 상태의 Promise 객체들의 배열이 찍히는 걸 알 수 있다..
map 함수로 brr를 선언하고 할당한 부분을 다시 보면, 비동기 함수인 asyncFunc의 결과 값을 기다리지 않고 단순히 호출에 그쳤기 때문에 결과 값이 배열에 저장되지 않고 asyncFunc의 초기 상태가 저장된 것 이다.
해결 방법
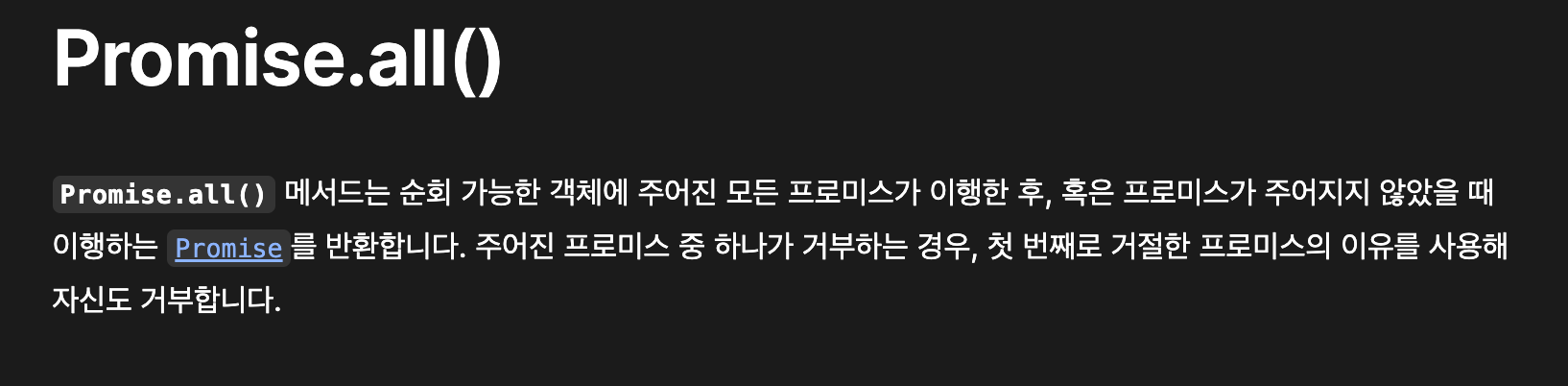
Promise.all() 을 이용하여 모든 Promise가 이행될 수 있도록 한다.
const brr = await Promise.all(
arr.map(async (id) => await asyncFunc(id))
);
console.log(brr);기존의 코드를 위처럼 수정하면 Array.map 내에서 async, await를 제대로 사용할 수 있다.
console
['name1', 'name2', 'name3' ...]'기술' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [yarn berry + vscode] yarn berry 적용 방법 (with vscode setting) (6) | 2023.01.17 |
|---|---|
| [yarn berry + Next.js + TypeScript] React Testing Library 적용하기 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
| [JavaScript] truthy, falsy 값 판별하는 간단한 방법 (0) | 2023.01.08 |
| [React + TypeScript] 무한 스크롤 구현하기 (0) | 2023.01.04 |
| [Next.js + TypeScript] Google Analytics 적용 방법 (2) | 2022.09.26 |


댓글 영역